General Data Protection Regulation
• Help you to Build Trust among your customers
• Help you to do Things in right way
• Protecting and safeguard you to attain GDPR compliance

GDPR: General Data Protection Regulation
Why Privacy will become even more important? In a world where more than half the population is online and everything is getting digitised as a matter of convenience and for that matter it is a way of life. Customers today uninhibitedly are sharing and receiving information while using the internet for entertainment, banking, healthcare, and utility purposes consequently continuously adding to a large pool of Data. In a quest to expand the market of products and services, many business entities are now implementing emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning on this customer-generated data to procreate value and insights. As the magnitude of Data increases, there will be a requirement for more sophisticated IT systems to extract value while maintaining privacy. The General Data Protection Regulation paved its way in the wake of emerging Data priorities of organisations in light of safeguarding rights of customers by imbibing a sense of accountability in the way personal Data is shared and used by the organisations.
Emergence of GDPR : After a fair deliberation, on December 15th, 2015, following three years of drafting and negotiations, the European Parliament and Council of the European Union reached an informal agreement on the EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). The objectives of GDPR are to reinforce Data Protection rights if Individuals, facilitate the free flow of personal data in the digital market and reduce the administrative burden. On April 14th, 2016, the Regulation and the Directive were adopted by the European Parliament with the provision of two year window for its implementation from the date of applicability of same. The General Data Protection Regulation supersedes in entirety the 1995 General Data Protection Directive w.e.f May 25th, 2018 and applies directly to each of the 28 EU Member States.
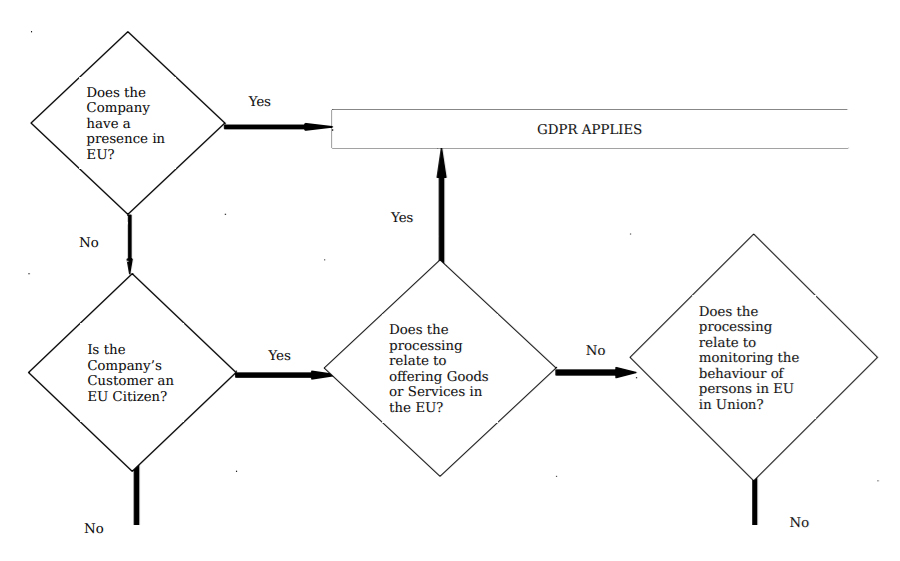
What is GDPR and to Whom it applies: GDPR is an omnibus regulation, by which the EU intends to strengthen and unify Data Protection within the European Union. It applies to any organisation regardless of geographic location that controls or processes the Data of an EU resident. The General Data Protection Regulation dictates what Data can be collected, the need for explicit consent to gather such Data, requirements to disclose any breaches of data, and stronger powers to substantially penalize organizations that fail to protect the Data for which they are responsible. GDPR is attracting significant attention as it introduces provisions for a number of new rights for Data subjects and several obligations which directly impact Data Controllers and Data Processors. Failing to do so will be severely dealt with steep penalties amounting to Twenty Million Euros or 4% of the annual Global revenues or whichever is higher.
The General Data Protection Regulation focuses on the processing of Data by automated means but can also relate to Data that forms a part of a non-automated filing system. GDPR applies in three circumstances:
- Establishment and processing of personal information in the union;
- The monitoring of the behaviour of Data Subjects as far as their behaviour takes place within the Union;
- Organization offering of Goods or Services, irrespective of whether a payment of the Data subject is required, to Data Subjects in the Union.
Key Changes Proposed by the GDPR:
➢ Hefty Penalties: Breach of the GDPR will result in substantial fines up to Euro 20,000.00 or 4% of annual worlwide turnover, whichever is greater
➢ Expanded Scope: Applies to all Data Controllers and Processors established in the EU and organizations that target EU citizens
➢ Mandatory Appointment of Data Protection Officers (DPOs): DPOs must be appointed if an organization conducts large scale systematic monitoring or processing of large amount of sensitive personal Data
➢ Obligatory Breach Notification: Notify supervisory authority of Data Breaches “without undue delay” or within 72 hours, unless the breach is unlikely to be a risk to individuals. If there is a high risk to individuals, they must also be informed
➢ Stringent consent requirement: Consumer consent to process Data must be freely given and for specific purposes. They also must be informed of their right to withdraw their consent. The consent must be “explicit” in the case of sensitive personal Data or transborder Data flow
➢ Risk based Privacy Impact Assessment: Organizations must undertake Privacy Impact Assessments when conducting risky or large scale processing of personal Data
➢ Broadened Data Subject rights: Organizations should have processes to manage the below given new rights:
➢ The right to be forgotten: The right to ask Data Controllers to erase all personal Data without undue delay in certain circumstances
➢ The right to Data portability: Where individuals have provided personal data to a service provider, they can request the provider to “port” the Data to another provider, if technically fesible
➢ The right to object to profiling: The right not to be subject to a decision based solely on automated processing
➢ Adequate protection for cross-border transfers: The GDPR allows data transfers to countries that provide “adequate” levels of personal Data protection. Transfers to non-EU states without an adequate level of personal protection is only permitted, when guarantee on Data protection is provided-such as standard contractual clauses or binding corporate rules (BCRs’)
➢ Obligations on Processors: The new Regulation entails new obligations on Data Processors. Processors become an officially regulated entity
➢ Privacy by Design and Default: Data protection safeguards must be built into products and services from the earliest stage of development. Privacy settings must be set at a high level by default. The very notion of Data protection by default includes Data minimization principles e.g. obtain and store only the necessary personal Data
➢ Accountability and Data Governance: Organizations must prove that they are accountable by:
➢ Establishing a culture of monitoring, reviewing and assessing data processing procedures
➢ Building inherent safeguards within Data processing activities
➢ Documenting Data processing policies, procedures and operations that must be made available on request to the Data protection supervisory authority
➢ Preparing Data inventories and Data flow Diagrams for processes that deal with personal Data
➢ Ensuring the accuracy of personal Data: And enabling it to be erased or rectified. Organizations will need to take steps to ensure that the personal Data held by them is accurate and can be corrected if errors occur
➢ Limiting the storage of personal Data: Organizations will need to ensure that they retain personal Data only for as long as necessary to achieve the purposes for which the Data was collected
➢ Ensuring security, integrity and confidentiality of personal Data. The Organization must take steps to keep personal Data secure through technical and organizational security measures.
Early Bird advantages and incentives of GDPR compliance
Organizations which have started their readiness and compliance journey will be successful in differentiating themselves from their competitors by proactively developing trust with their customers on handling sensitive Data. These strong trustworthy customer relationships present opportunities for organizations to retain or increase their revenues from customers dealing with personal Data from EU. Moreover, GDPR compliance and readiness ensues business edge.
Key Safeguards to be adopted by Organizations
The General Data Protection Regulation or GDPR underlines multiple changes which says that there are certain key safeguards that organizations can take to ensure that they start their compliance journey for GDPR: Identification of Personal Records of Processing Activities Implement Privacy by Design and Default Ability to Ensure ongoing confidentiality, integrity, availability and resilience of processing services. Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA) and Gap Assessment can be adapted to identify the current state.
